
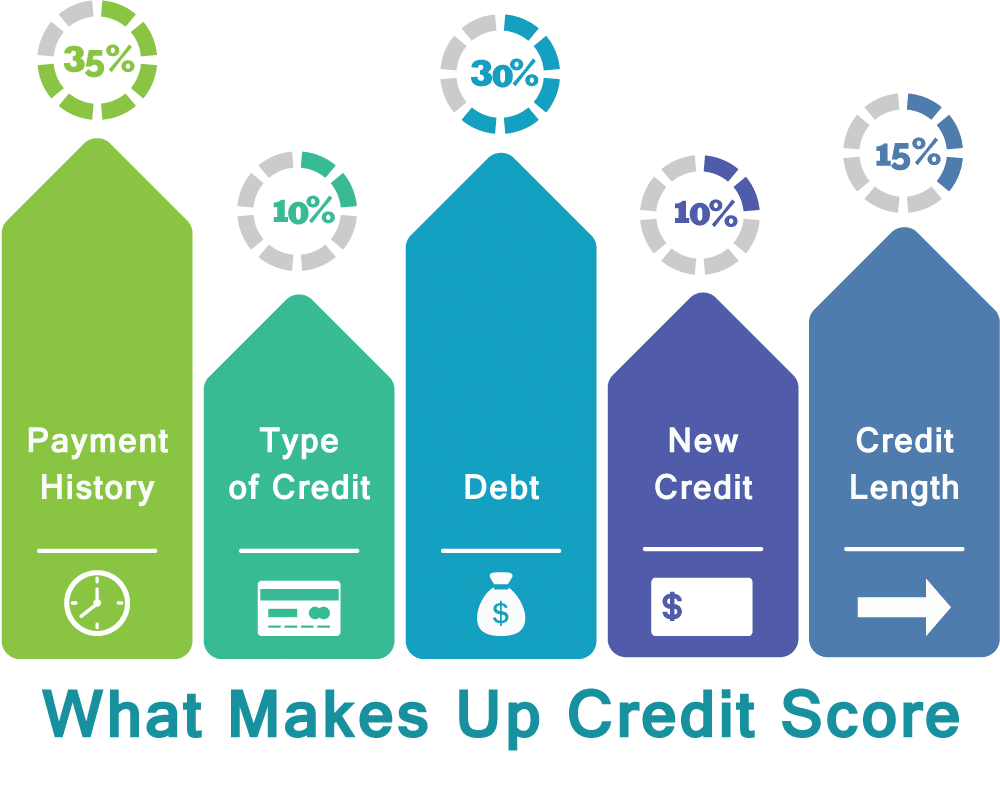
The first two factors in your credit report make up nearly two-thirds of your total score. These are payment history and debt. 15% of this is dependent on the length and complexity of your credit history. Next, consider the types of credit that you have used. Your score will be higher if you take care to avoid high credit balances and make timely payments.
Payment history
Your payment history is a key factor in determining whether you are eligible for a loan. Credit scoring models consider several factors when determining your credit score. They also take into consideration how prompt you pay your bills. The number and size of late payments you make can affect your overall score. Avoid lowering your score by paying all bills on time.
A late payment is a big factor in lowering your score, and is generally considered to be 30 days late. Your score will be affected if you pay late even for a few days. This mark will stay on credit reports for seven years. Although lenders will not report payments more than 30 days late, they will charge you a fee if you miss your due date.
Debt
Debt is an important part of your credit score, making up 30% of the total. It is therefore important to keep track and pay as much as you can each month. The amount of your credit can be affected by several factors. It is important to not charge things that you don't really have the cash for. Your score will drop if your owing more than what you can afford.

To improve your credit score, you should pay off as much debt as possible. It is best to keep your outstanding balances below 30% of your total credit limit. This shows lenders that you are responsible when it comes to debt. If you have a great payment history, you can also increase credit limits. Lenders won't increase your credit limit if your payment history is excellent.
Combination of credit
Your credit score is affected by the type of credit you have. You may have a good mix of revolving and installment credit, but it's not enough to simply have one type. A mix of credit types shows that you can manage multiple types of accounts and pay them off in full each month. This credit mix is not recommended for people with a history of bankruptcy, late payments, excessive credit usage, or bankruptcy.
About 10% of your credit score comes from the mix of credit types that you have. This mix of accounts can include installment loans, retail accounts, finance company accounts, and mortgage loans. Diverse credit types help lenders see that you can manage financial obligations and improve score.
Length of credit history
It is important to look at the length of credit history when building credit scores. Your credit score will increase the more you have credit history. This factor is calculated by adding up the ages of all your accounts and dividing them by the number of accounts you have. Eight years is the average credit history. Your credit score considers not only the total credit history but also the age of each credit account as well as the date you last used it.
The complicated algorithm used to calculate your credit score takes into account a variety of factors including the age of your accounts. Credit scoring models are built on the basis of your oldest account.
Debt to credit limit
Your credit score includes several factors such as the debt to limit ratio. Your debt-to credit limit ratio is a percentage your total credit line. This number is often used in scoring formulas by lenders. Lenders prefer to see a low debt-to-limit ratio. High debt-to-limit ratios are a sign you are a risky borrower. Credit scores can be affected.
Calculating your debt-to-credit limit ratio involves dividing the total amount in debt by the credit you have. A debt-to-limit ratio below 30% is a good goal. If you exceed that number, your credit score could be affected and you might be unable to purchase a home or refinance your existing loan.